DISCOVERY OF INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID DERIVATIVES CONTAINING 1,3,4-THIADIAZOLE THIOETHER AND AMIDE MOIETIES AS NOVEL ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS
Keywords:
thioether, amide, plant bacterial disease, indole-3-acetic acid, 1,3,4-thiadiazoleAbstract
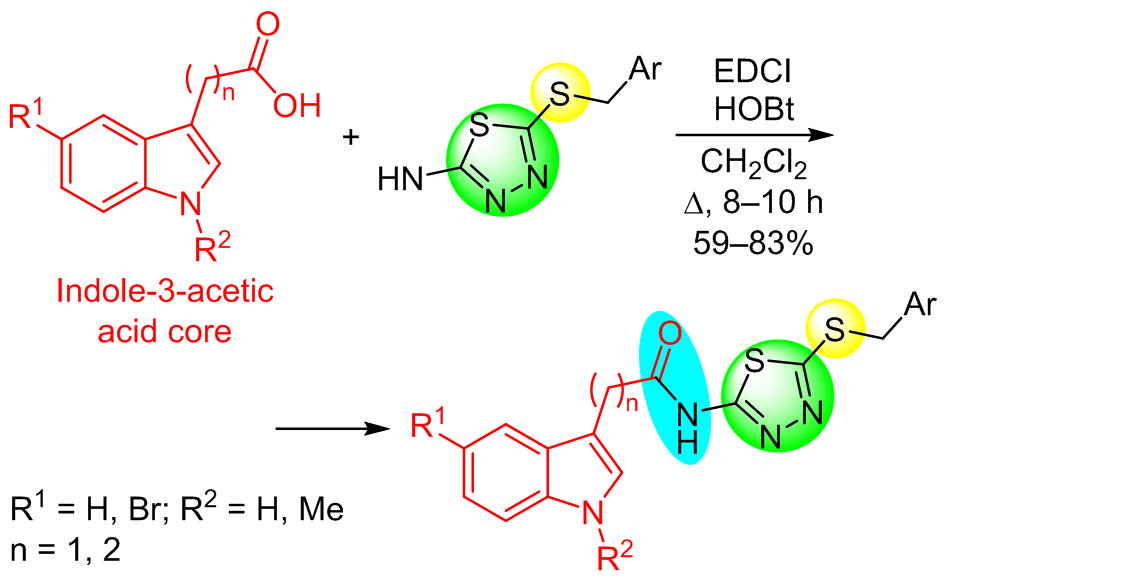
A series of twenty one novel compounds derived from indole-3-acetic acid, the structure of which includes 1,3,4-thiadiazole, thioether, and amide moieties were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for their in vitro antibacterial activity against three bacterial strains. The bioassay results showed that among the synthesized compounds, N-{5-[(2-fluorobenzyl)sulfanyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl}-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanamide demonstrated the best inhibition rate against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and N-{5-[(4-chlorobenzyl)sulfanyl]-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl}-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanamide possessed the best inhibition rate against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, in all cases superior to that of bactericides thiodiazole copper and bismerthiazol.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Versions
- 2024-03-26 (2)
- 2024-03-26 (1)
