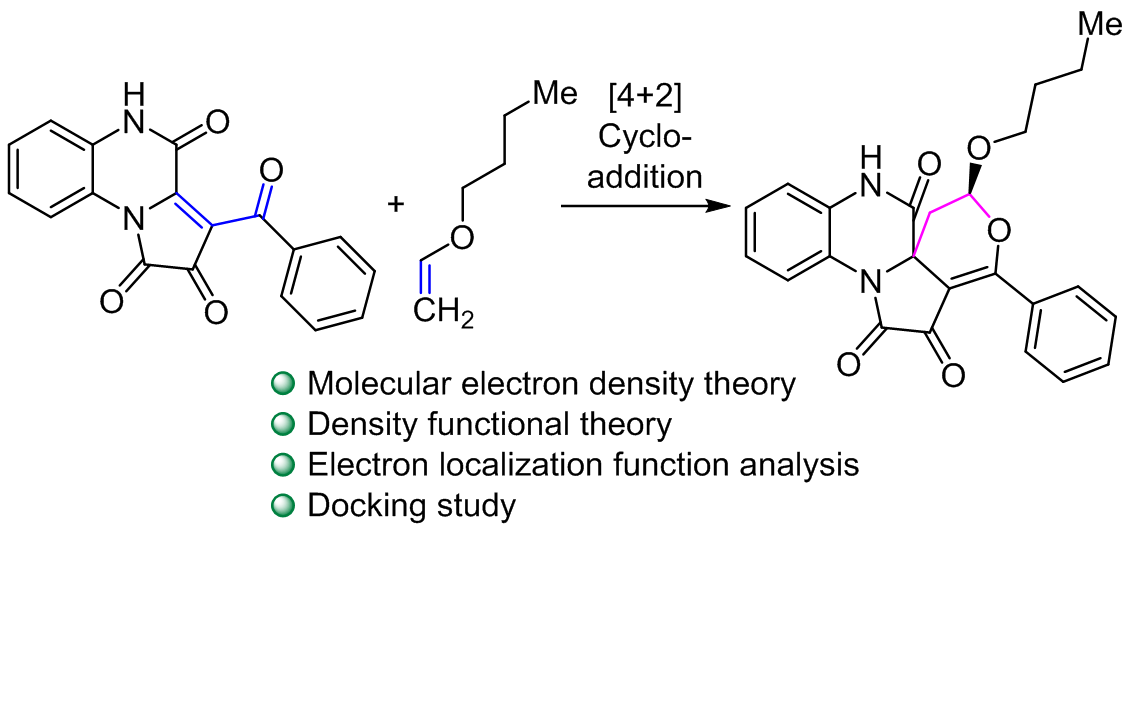
Molecular docking, exploring diverse selectivities and mechanistic insights in the cycloaddition reaction between 3-benzoylpyrrolo[1,2-<i>a</i>]quinoxaline-1,2,4(5<i>H</i>)-triones and butyl vinyl ether
Ключевые слова:
cycloaddition, ELF, MEDT, molecular dynamics, regiospecificityАннотация
Molecular electron density theory was used to examine the [4+2] cycloaddition between butyl vinyl ether and 3-benzoylpyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxaline-1,2,4(5H)-trione. Butyl vinyl ether behaves as a nucleophile, whereas 3-benzoylpyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxaline-1,2,4(5H)-trione behaves as an electrophile, according to the analysis of conceptual DFT indices. The results consistently align computational activation and reaction energies with experimental findings, confirming that this cycloaddition reaction exhibits chemo-, regio-, and stereospecificity. Based on the electron function analysis, this cycloaddition reaction follows a mechanism that can involve either a one-step or asynchronous process. Furthermore, a docking study was performed on the predominant product, which was anchored in the primary protease of VEGFR-2. As a result, these compounds demonstrated increased stability and greater affinity for binding to VEGFR-2, attributed to their interactions with a larger number of residues through hydrophobic interactions when compared to vandetanib.